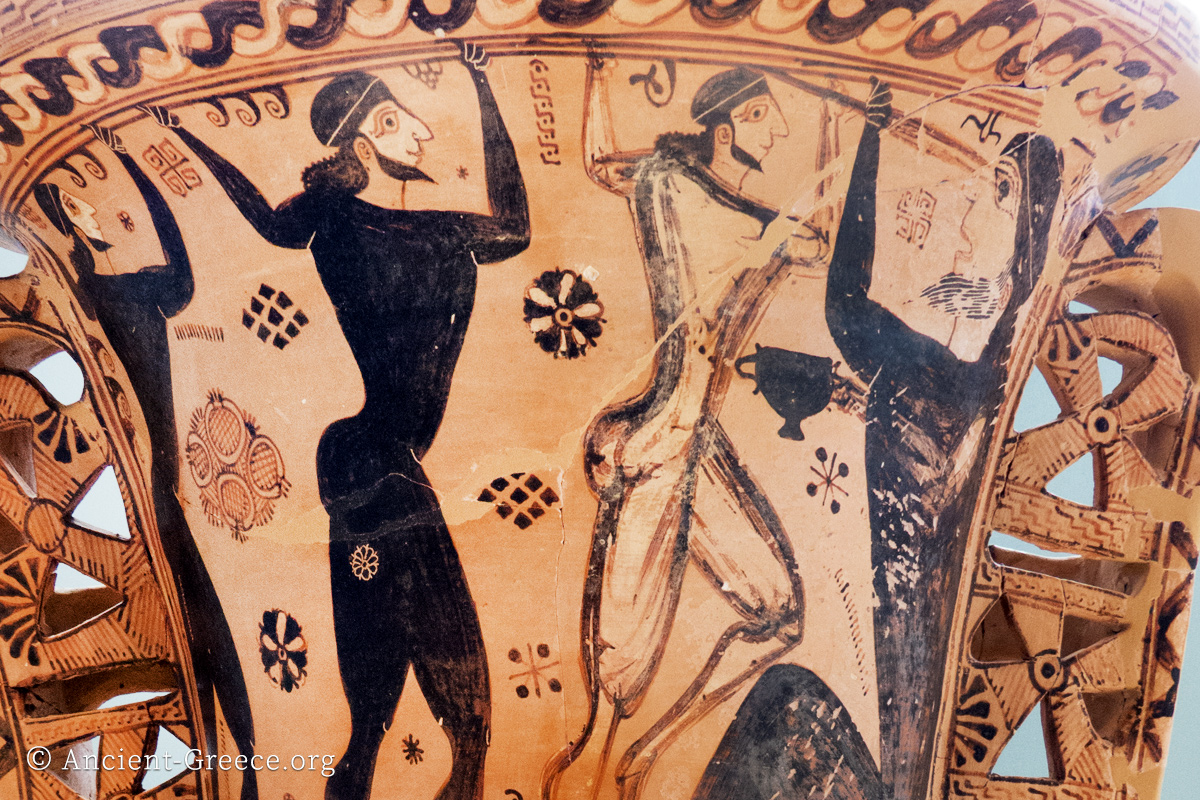History and Culture
-

Agora of Athens History
Read more: Agora of Athens HistoryPrehistory to Iron Age The Agora of Athens has been in use since the late Neolithic era, and it was used as a cemetery during the Mycenaean and the later Iron Ages. Excavations have unearthed around 50 tholos…
-

Ancient Greece Timeline
Read more: Ancient Greece TimelineChapters This history of Ancient Greece is divided into the following chapters: Related Pages The official ancient-greece.org Youtube Channel
-

Ancient Greece: Introduction and Significance
Read more: Ancient Greece: Introduction and SignificanceThe ancient Classical and Hellenistic eras of Greece, between the 5th and the 1st century BCE, are undoubtedly the most splendid. They left behind an enduring heritage of ideas, concepts, and art that have been influential for centuries…
-
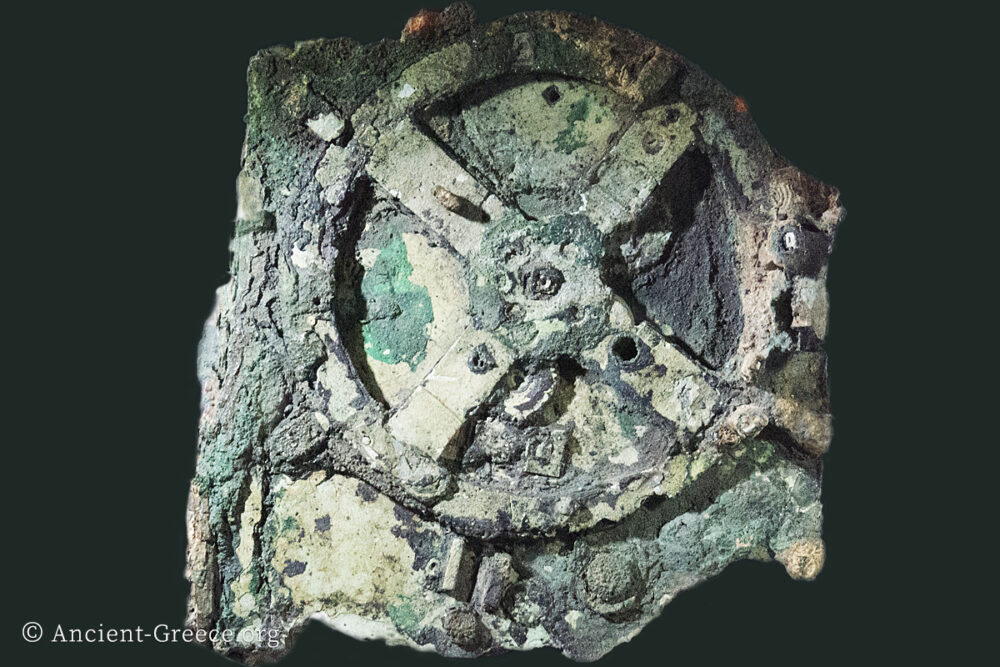

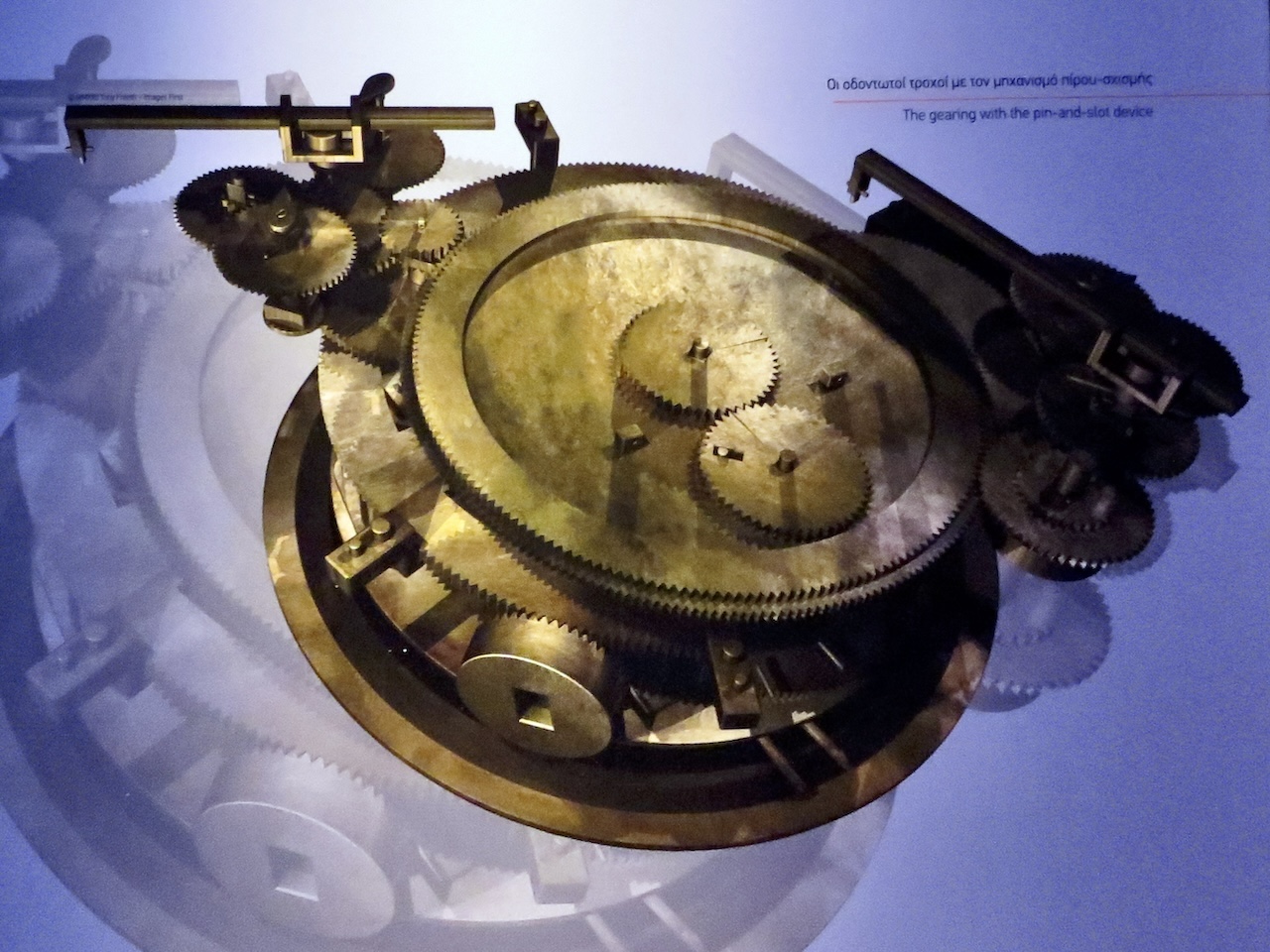
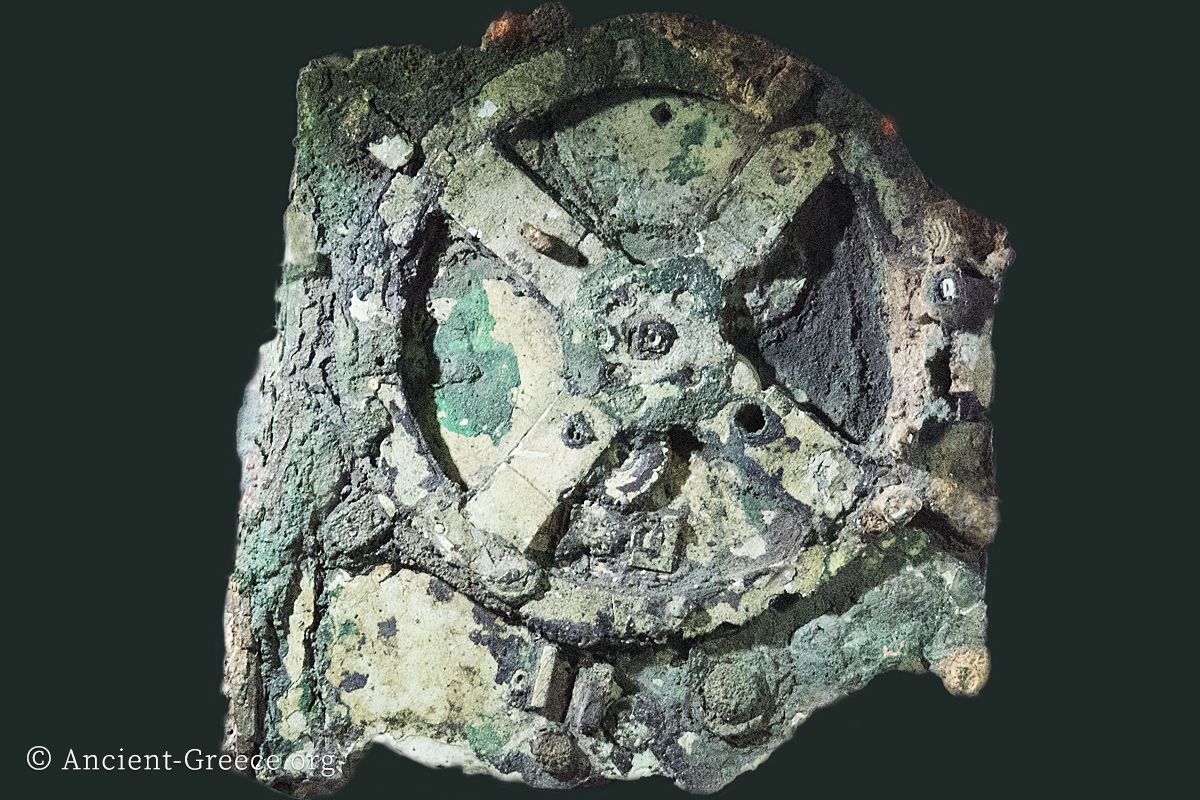
The Antikythera Shipwreck
Read more: The Antikythera ShipwreckThe Antikythera Shipwreck is a 1st century BCE underwater shipwreck and archaeological site, located 25 meters from the coast of Antikythera island, Greece, at a depth of about 50 meters. The cargo ship’s final voyage started in an…
-
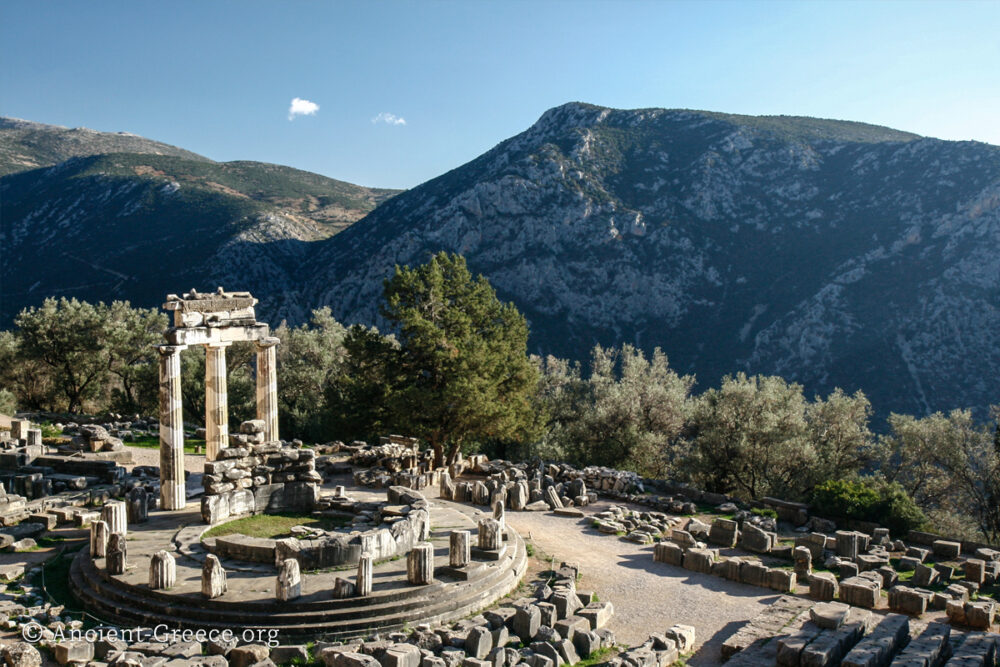

Delphi History
Read more: Delphi HistoryApollo squinted in the bright sunlight and calmly tensed his muscles as he pulled his bow. He released his arrows one after the other until Python’s blood was spilled and his life escaped in the thin air. Python-dragon,the…
-

Dodona History
Read more: Dodona HistoryDodona (Δωδώνα, Δωδώνη, Dodoni) is an important ancient Greek oracle, second in fame only to Delphi. It is located in a strategic pass at the eastern slopes of the imposing Mt. Tomaros, close to the modern city of Ioannina…
-
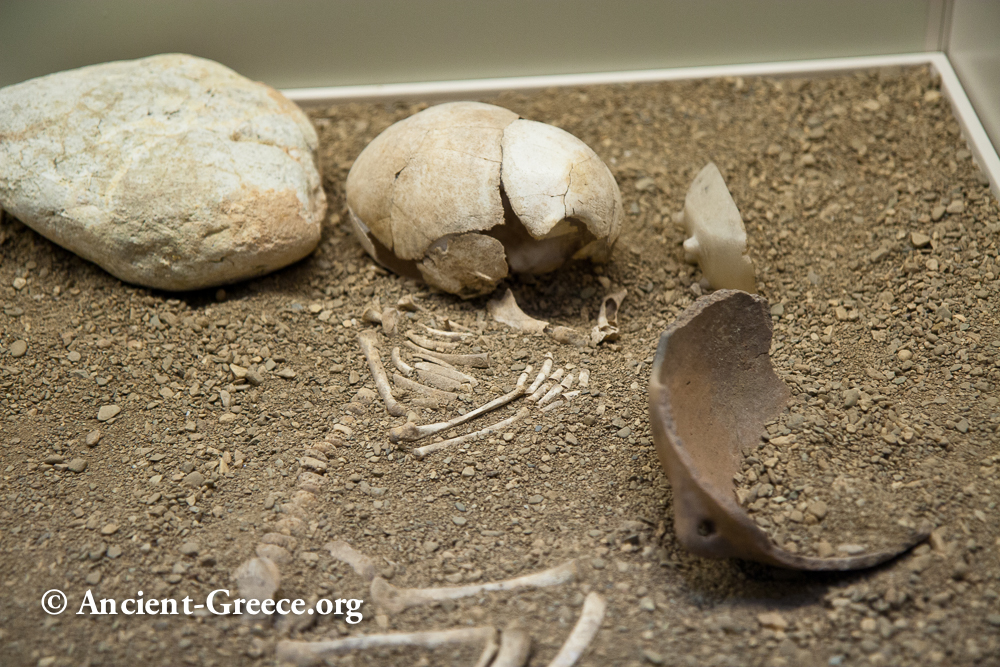

Franchthi Cave History
Read more: Franchthi Cave HistoryFranchthi Cave (Φράγχθι Σπήλαιον) in Argolis, Peloponnese, Greece offers a rich unbroken record of human habitation from the Paleolithic era (at least since 38000 BCE) to the end of the Neolithic period and beyond. Location Francthi Cave is…
-
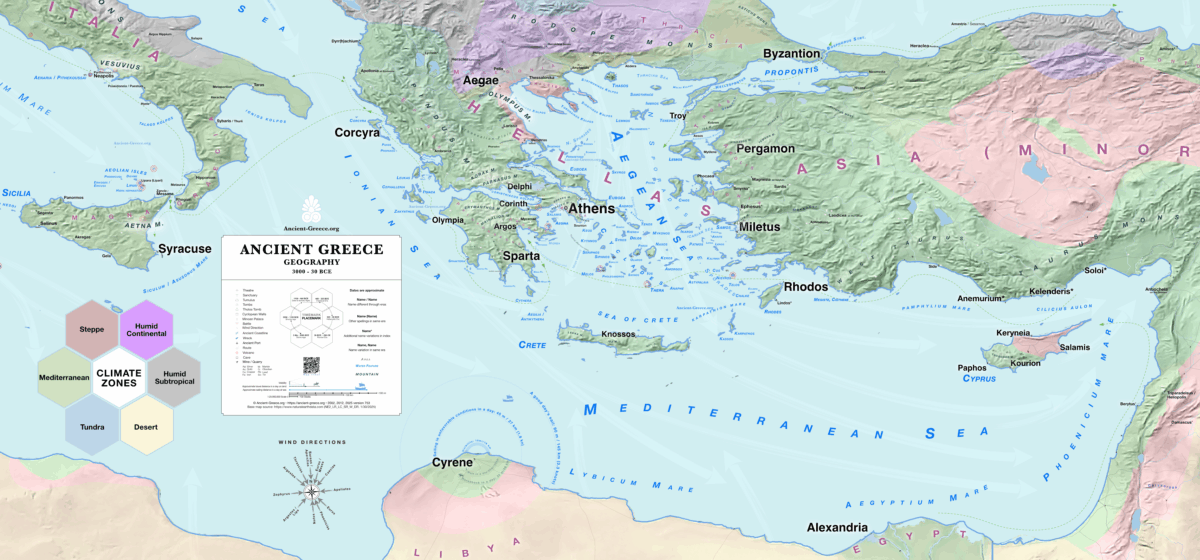
Geography
Read more: GeographyThe Mediterranean Sea The position of Greece at the crossroads between Africa, Asia, and Europe has undeniably played a large role in its diverse and often turbulent history. Protruding from Europe, Greece hangs precariously southward from the end…
-
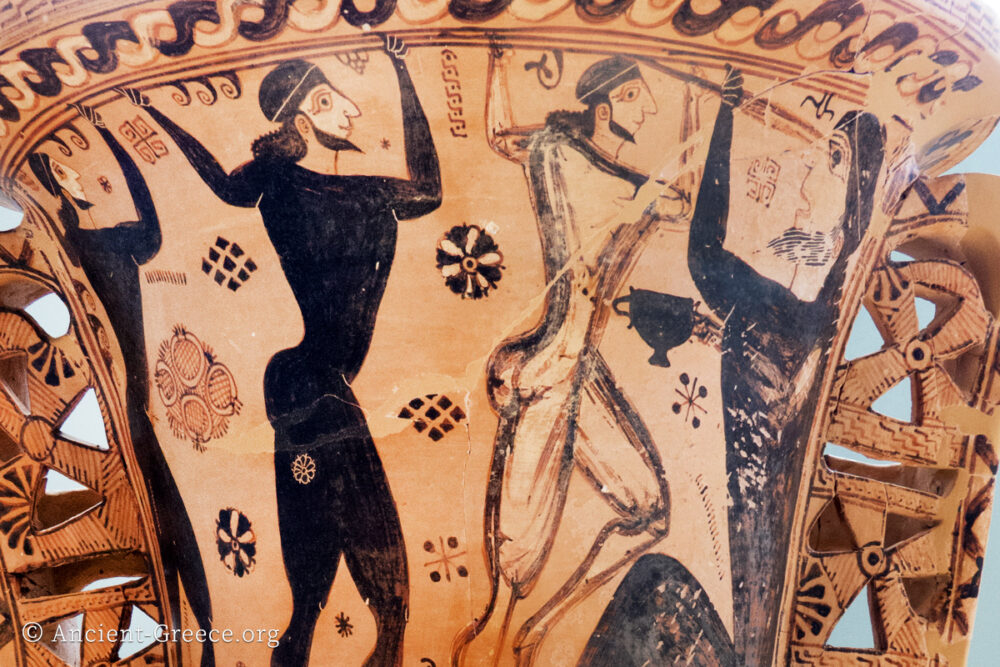
Greek Mythology
Read more: Greek MythologyThe ancient Greek spiritual beliefs, religion, and oral tradition are all reflected and formulated through rich myths and legends that besides entertainment provided an articulation of Greek civilization’s moral fiber, as it evolved over the centuries. Mythology is…
-

History of Ancient Greece: Periods Overview
Read more: History of Ancient Greece: Periods OverviewIllustrated Overview Historical Periods Ancient Greek history is generally divided into the following eras: Stone Age (circa 400 000 BP – 3000 BCE)> Paleolithic (circa 400 000 – 13 000 BP)> Mesolithic (circa 10 000 – 7000 BCE)>…