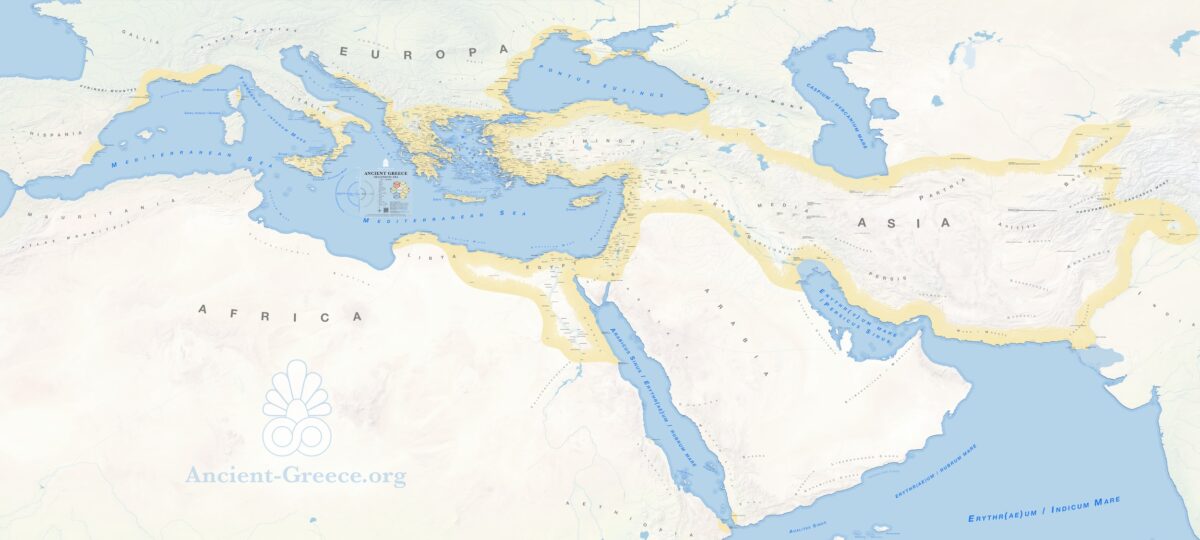
On this page:
Illustrated Overview
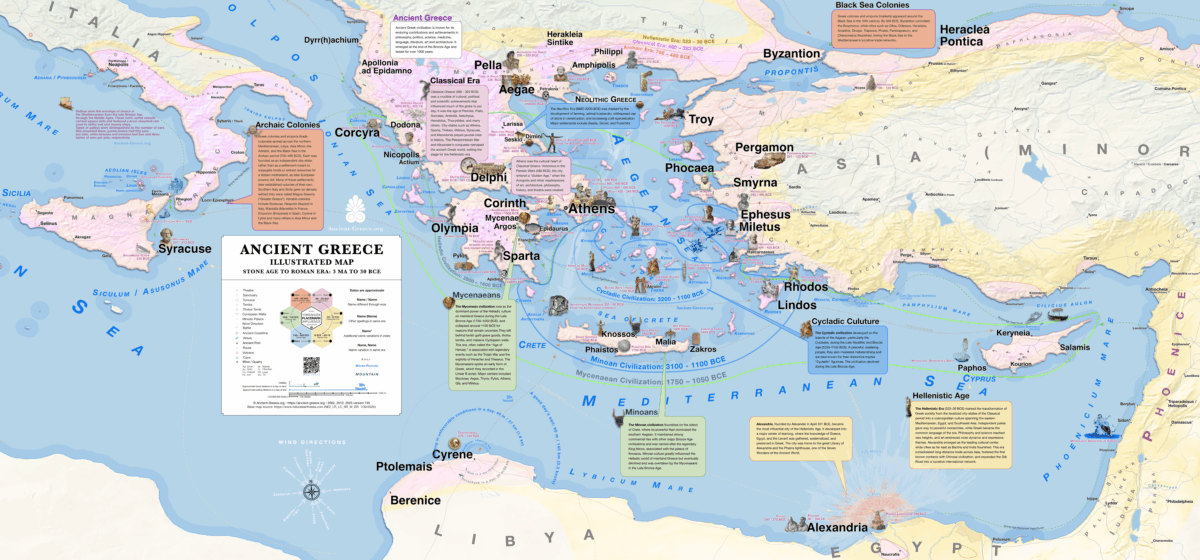
Historical Periods
Ancient Greek history is generally divided into the following eras:
Stone Age (circa 400 000 BP – 3000 BCE)
> Paleolithic (circa 400 000 – 13 000 BP)
> Mesolithic (circa 10 000 – 7000 BCE)
> Neolithic (circa 7000 – 3000 BCE)
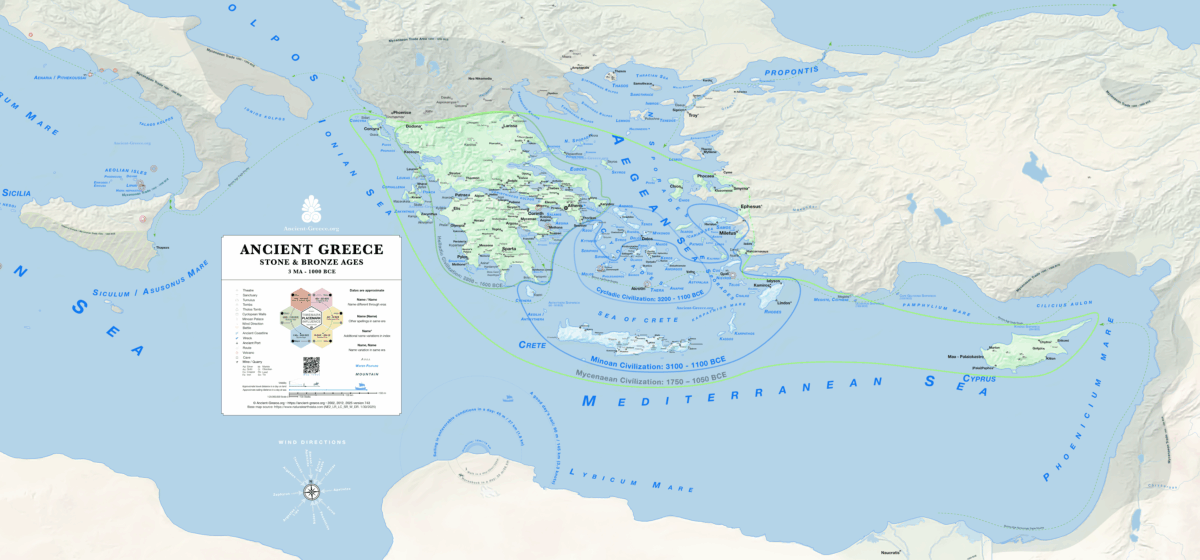
Bronze Age (circa 3300 – 1150 BCE)
> Cycladic (circa 3200 – 1100 BCE) in the Aegean islands
> Minoan (circa 2600 – 1200 BCE) in Crete
> Helladic (circa 2800 – 1600 BCE) on the mainland.
> Mycenaean or Late Helladic (circa 1600 – 1100 BCE)
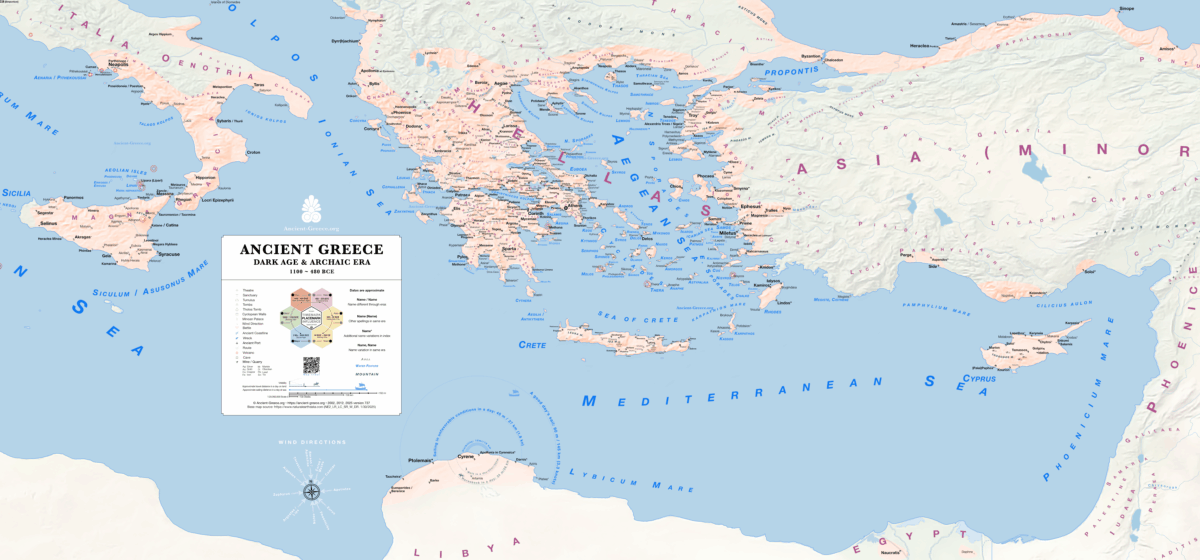
Iron Age
> Dark Ages (circa 1100 – 700 BCE)
> Archaic (circa 700 – 480 BCE)
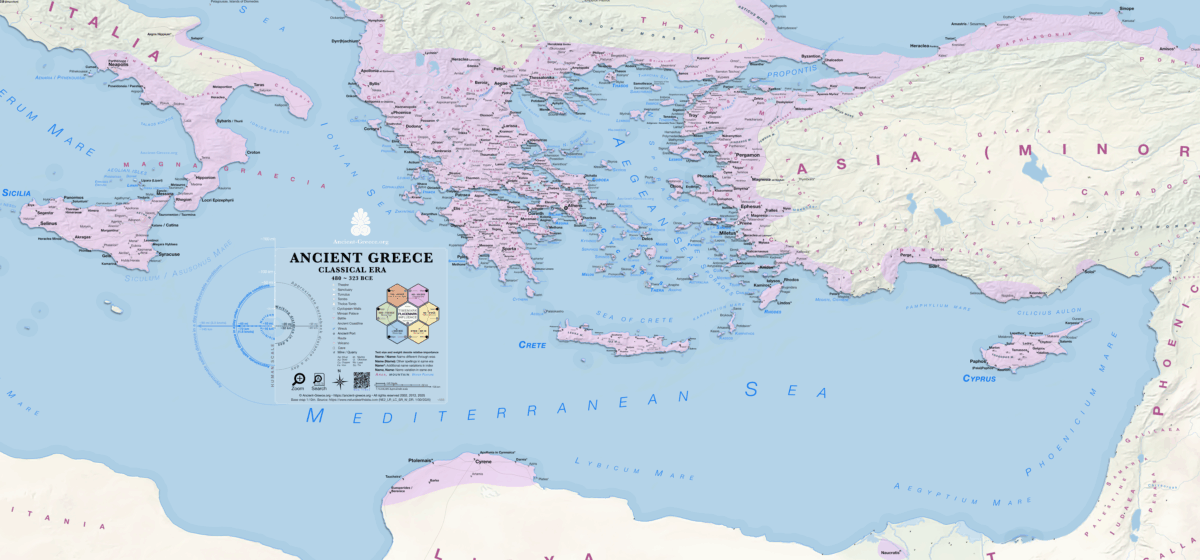
> Classical (480 – 323 BCE)
> Hellenistic (323 – 30 BCE)
Each era had its own unique cultural characteristics, and the transition between them was often tumultuous.
Maps by Period
Chapters
This history of Ancient Greece is divided into the following chapters:
- Timeline
- Introduction
- Overview
- Geography
- Stone Age
- Bronze Age
- Dark Ages
- Archaic Era
- Classical Era
- Hellenistic Era
Greek is one of the most influential languages in the world, and the ancient Greeks were prodigious writers. These are four examples of writing from ancient Greece.
Examples of scripts by era
From top left:
• The Phaistos Disk. 1700 BCE Age
• Linear A script tablet. 1450 BCE
• Linear B script tablet. 14-13 c. BCE
• The Dipylon Oenochoe. 740 BCE
• Early Greek Alphabet. 7th c. BCE
• Ostracon from Athens. 5th c. BCE.
• Silver mines leasing report. 367-6 BCE
• Macedonian votive shield. 274 BCE
• Antikythera Mechanism. 2nd c. BCE
• The Rosetta Stone. 196 BCE
• Delphi musical notation. 128 BCE
Related Pages